Introduction
Arcade machines have fascinated gamers for decades, but behind every great arcade experience lies a critical component—the Printed Circuit Board (PCB). The PCB is the heart of an arcade machine, responsible for processing game logic, graphics, sound, and input controls. This guide provides a beginner-to-intermediate breakdown of what an arcade PCB is, how it works, and its essential components.
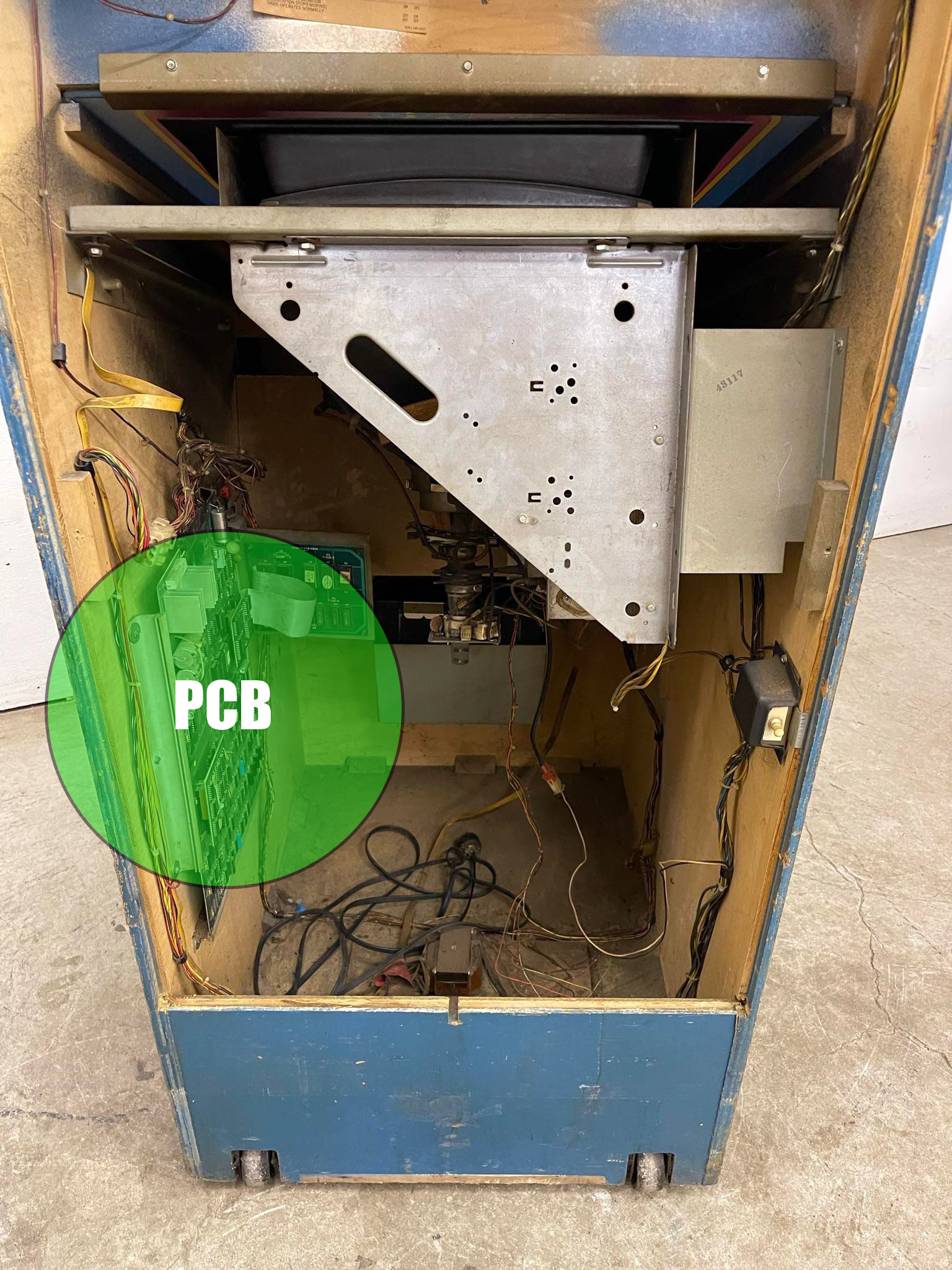

1. What is an Arcade PCB?
An arcade PCB is a dedicated circuit board that runs an arcade game. Unlike home console cartridges, which are interchangeable, a PCB is typically soldered or mounted directly inside the arcade cabinet.
Arcade PCBs vary in design and complexity, but they all serve the same purpose: running the game software, handling player inputs, and displaying visuals on the screen.
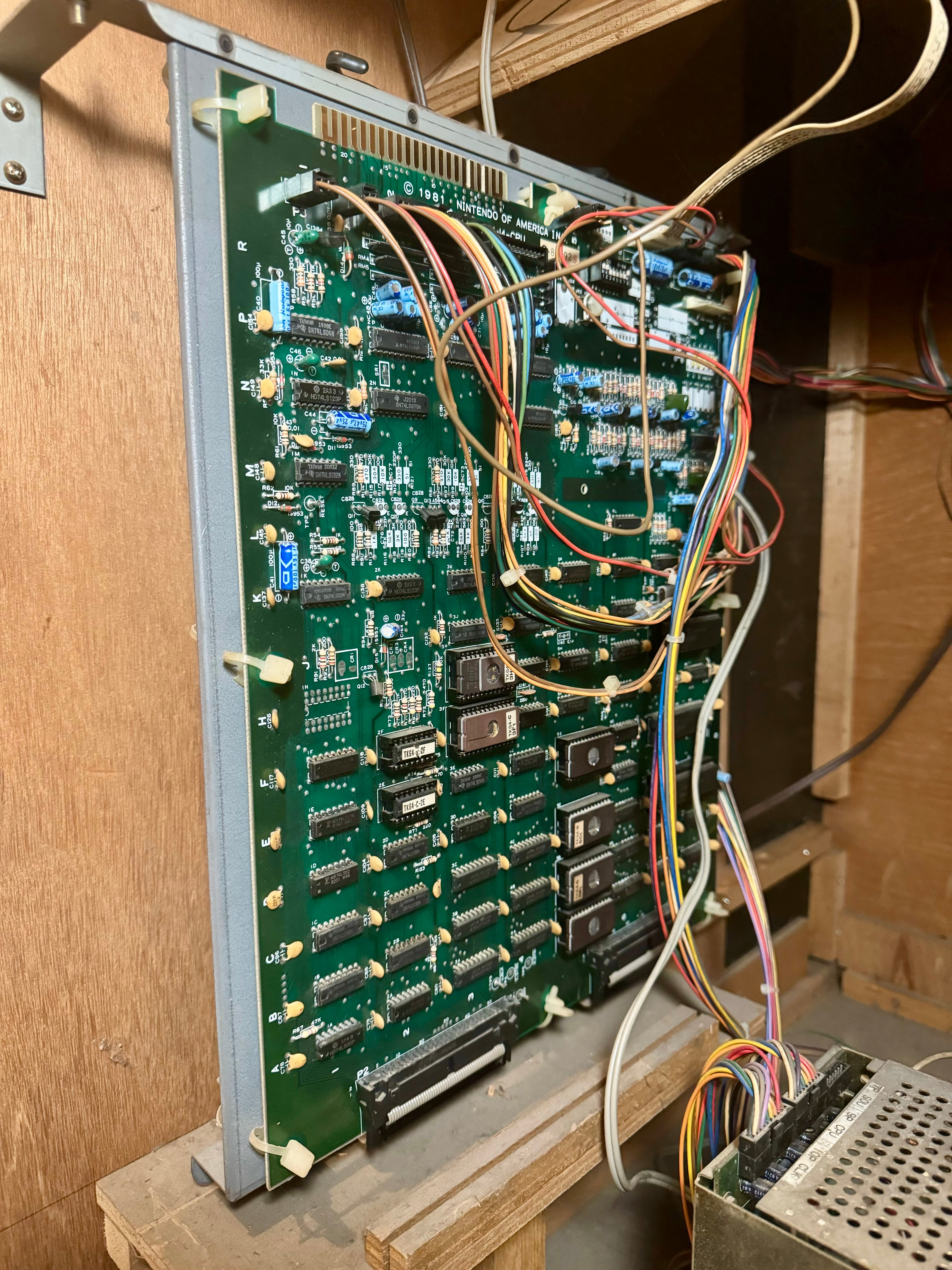
2. Key Components of an Arcade PCB
A PCB consists of several interconnected components that work together to run the game.
The CPU (Central Processing Unit)
The CPU is the brain of the arcade PCB, handling all calculations, AI, and physics. Different arcade games use different CPUs, each optimized for their specific hardware and game requirements.
Some of the most common arcade CPUs include:
- Zilog Z80 – Used in Pac-Man, Galaga.
- Motorola 68000 – Used in Street Fighter II, Final Fight.
- Hitachi SH-2 – Used in Sega’s Model 2 hardware.
ROM Chips (Read-Only Memory)
ROM chips store game code, graphics, and sound data. These chips ensure that the arcade machine always runs the same software each time it is powered on.
There are two main types of ROMs:
- EPROMs (Erasable Programmable ROMs) – Can be rewritten if needed.
- Mask ROMs – Permanently programmed at the factory.
For example, Capcom’s CPS-2 boards used encrypted ROM cartridges to prevent piracy.

RAM (Random Access Memory)
RAM is the temporary storage used during gameplay for:
- Storing game variables (e.g., player scores, character positions).
- Handling AI calculations for enemy movement and behavior.
- Video RAM (VRAM), which holds graphics data before it is sent to the screen.
Graphics & Sound Chips
Arcade games rely on specialized chips to generate visuals and audio.
- The Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) or Video Display Processor (VDP) renders sprites, backgrounds, and special effects. Systems like Namco’s System 11 and Sega’s Naomi had powerful GPUs for their time.
- Sound chips produce the background music, sound effects, and voice samples. Examples include the Yamaha YM2151 and OKI MSM6295, used in Mortal Kombat.
Custom & Security Chips
Some manufacturers implemented custom ICs (Integrated Circuits) to enhance gameplay with unique effects and prevent bootlegging.
One notable example is the Suicide Battery found in Capcom’s CPS-2 boards. If the battery died, the game would become unplayable due to encryption protections.
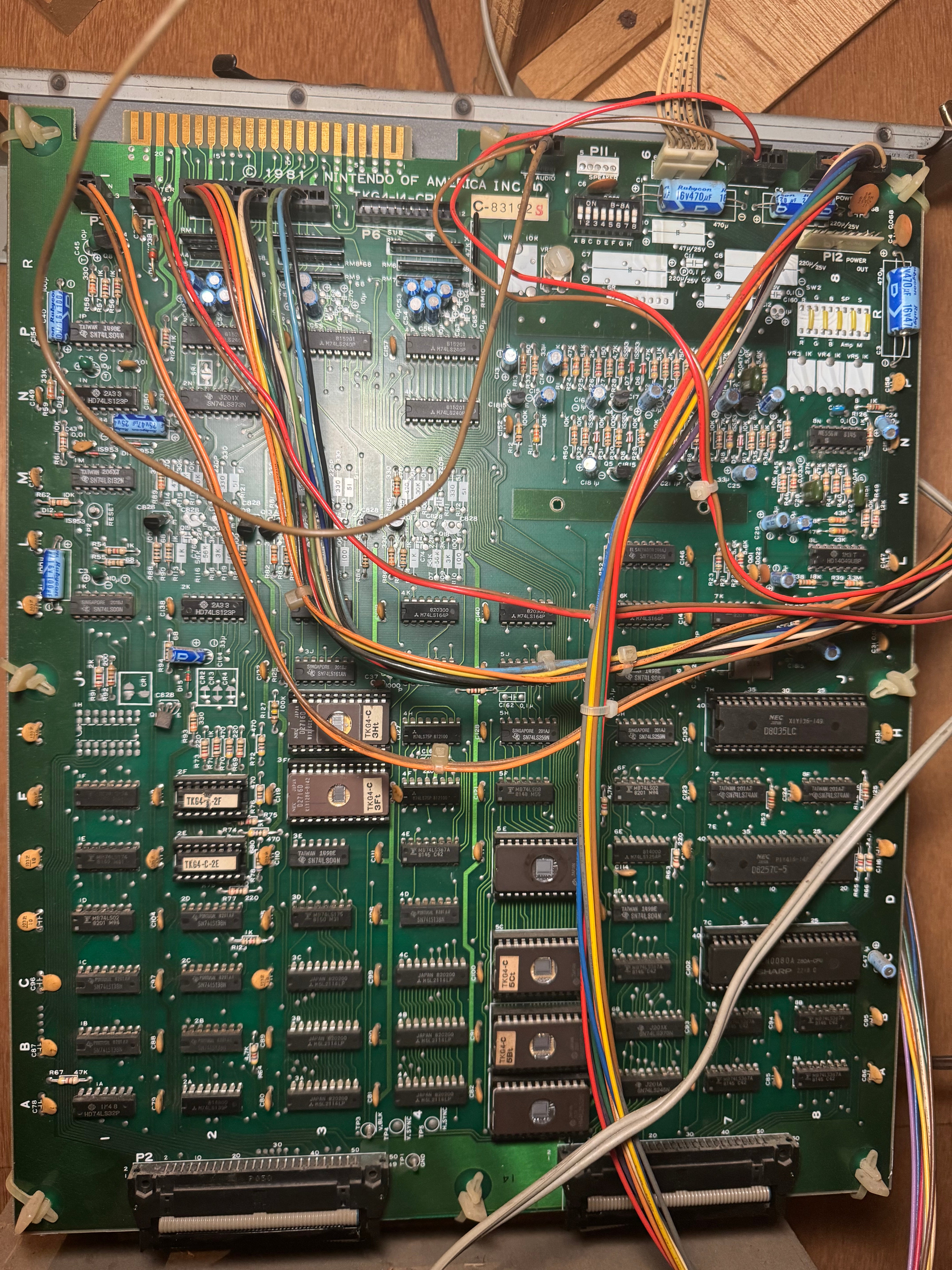
3. How an Arcade PCB Works in a Machine
When powered on, an arcade PCB follows a sequence of operations to run the game:
- Power is supplied from the arcade power supply unit (PSU).
- The CPU initializes the game software, processing player inputs and game logic.
- The graphics chip generates sprites and backgrounds and sends them to the monitor.
- The sound chip produces music and sound effects, playing them through speakers.
- The game runs in a loop, continuously updating visuals and responding to player input.

4. JAMMA vs. Non-JAMMA PCBs
What is JAMMA?
JAMMA (Japan Amusement Machine and Marketing Association) is a universal wiring standard introduced in 1985. Before JAMMA, each arcade game had unique wiring, making PCB replacements difficult.
With JAMMA, arcade operators could easily swap game PCBs without rewiring the cabinet.
JAMMA Benefits
- Uses a 56-pin edge connector for power, video, audio, and controls.
- Most arcade PCBs from 1985 onward followed this standard, including Street Fighter II, Mortal Kombat, and Metal Slug.
Non-JAMMA Systems
Some manufacturers, like Sega and Namco, used proprietary connectors for exclusive hardware.
- Sega Model 2 and Namco System 22 required unique connectors and specialized cabinets.
- Dedicated cabinets like Daytona USA and House of the Dead were built specifically for their respective PCBs.
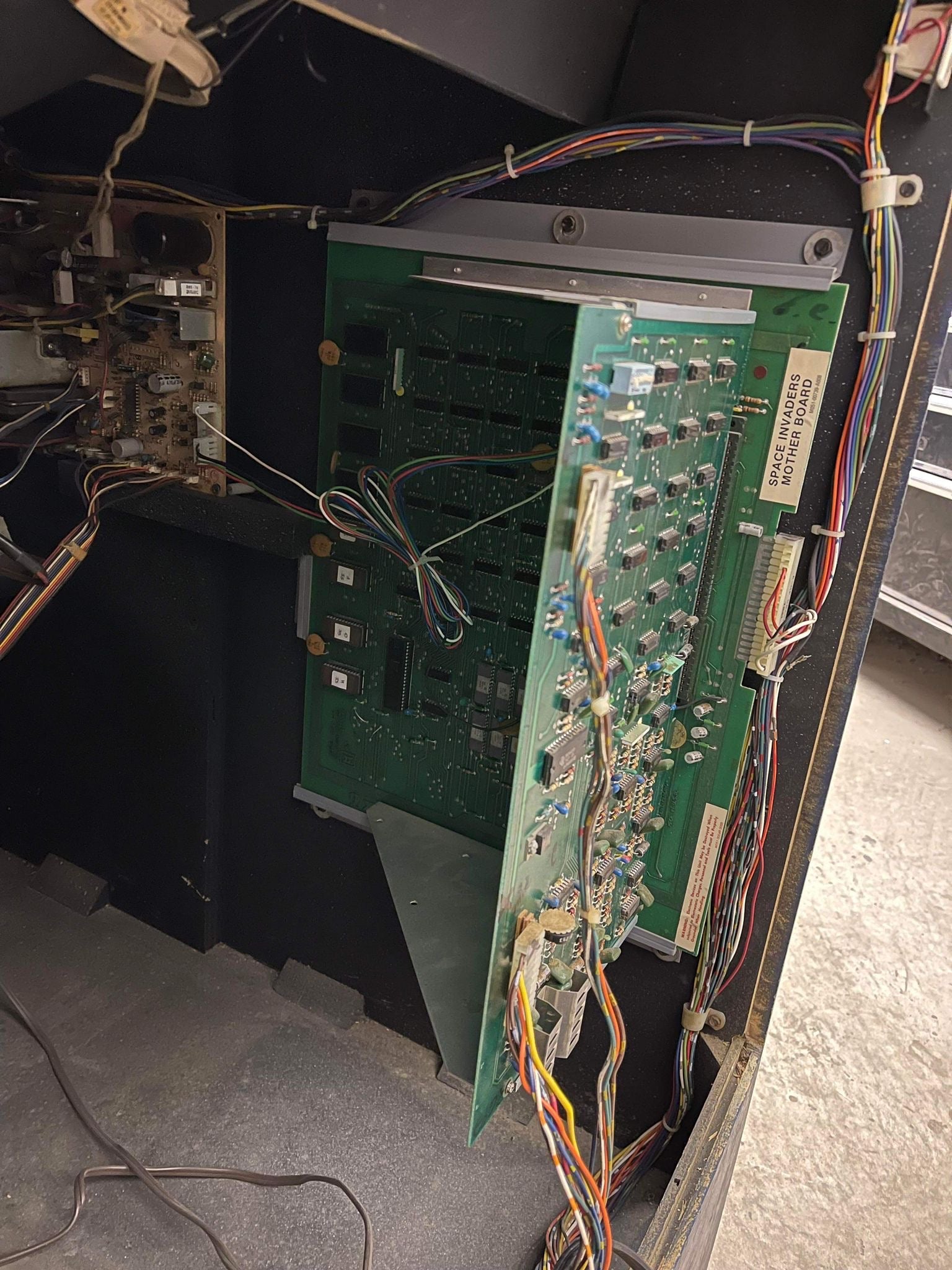

5. Common PCB Issues & Troubleshooting
Arcade PCBs, especially vintage ones, can develop problems over time.
Common PCB Issues
- No power or failure to boot – Often caused by power supply issues or bad capacitors.
- Glitched graphics – Could be faulty VRAM or corrupted ROMs.
- No sound or distorted audio – May be due to damaged sound chips or poor speaker connections.
- Unresponsive inputs – Could be caused by a faulty edge connector or wiring issues.
Diagnostic Tools
To troubleshoot PCB problems, arcade technicians often use:
- Multimeter – Checks voltage and continuity.
- EPROM Reader/Programmer – Verifies and reprograms game ROMs.
- Capacitor Tester – Identifies failing capacitors that may cause instability.
6. Restoring & Preserving Arcade PCBs
Restoring and maintaining PCBs is essential for preserving arcade history.
- Recapping (Replacing Capacitors) helps stabilize power delivery and extends the board’s lifespan.
- Reflowing Solder Joints can fix poor connections due to aging.
- Replacing Suicide Batteries is crucial for CPS-2 and other encrypted PCBs to keep them running.
- ROM Dumping & Cloning allows preservation of rare games by backing up software.

7. Conclusion
Arcade PCBs are the core of every arcade machine, responsible for everything from graphics to controls. Understanding how they function and how to maintain them is key for arcade preservation and repair.
Related Pages
- Ultimate Guide to ArcadeMachine Repair:Troubleshooting & Fixes
- What’s Inside an ArcadeMachine & How Does ItWork?
- Arcade Hardware Explained: Understanding CRT Monitors
- Arcade Hardware Explained: Understanding Power Supplies
Resources
- Arcade Game Service Manuals - PrimeTime Amusements
A comprehensive collection of digital service manuals for various arcade games, available in PDF format. - Arcade & Vending Equipment Service Manuals - Betson
An extensive library of service manuals for arcade games and vending machines from leading manufacturers. - The Arcade Manual Archive (TAMA) - International Arcade Museum
A premier technical manual resource offering a vast archive of manuals, circuit diagrams, and other materials related to arcade machine operation. - GameRepair.info - Arcade Repair Collaborative Manual
A collaborative manual created by collectors and operators, documenting repair tips and technical information for various arcade games and systems.

