Introduction
Arcade machines rely on Power Supply Units (PSUs) to provide stable electrical power to their components, including PCBs, monitors, and controls. A failing PSU can cause video glitches, sound issues, and even prevent a machine from booting up. Understanding how arcade power supplies work, diagnosing issues, and maintaining them is essential for keeping classic machines running smoothly.
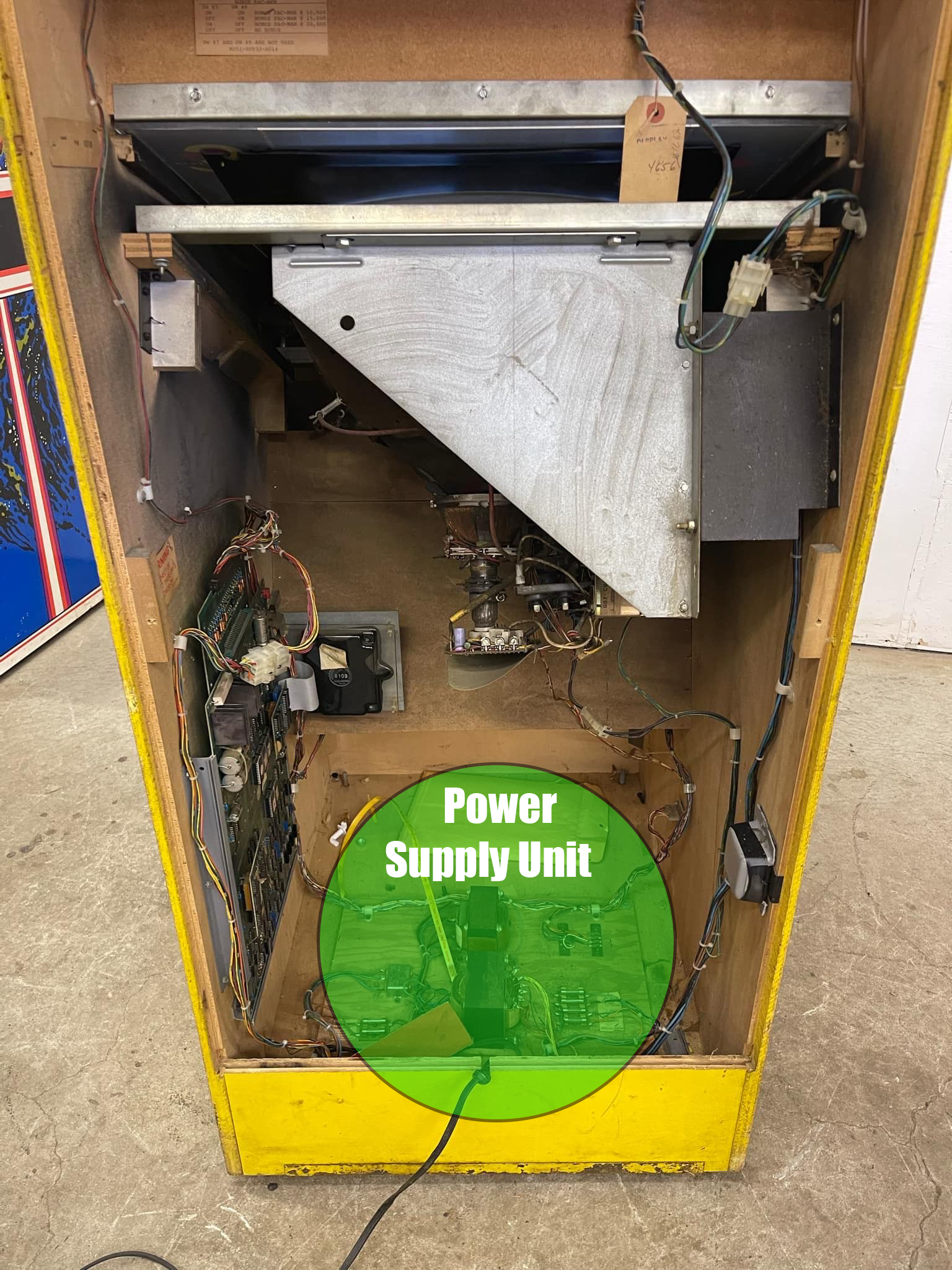
1. What is an Arcade Power Supply?
An arcade power supply (PSU) converts AC (Alternating Current) from the wall outlet into DC (Direct Current) voltages that arcade machines require. Unlike home gaming consoles, arcade cabinets use dedicated power supplies that must meet specific voltage and amperage requirements.
There are two main types of arcade PSUs:
- Linear Power Supplies – Found in older cabinets; use heavy transformers and are less efficient.
- Switching Power Supplies – Standard in modern cabinets; more efficient, compact, and reliable.
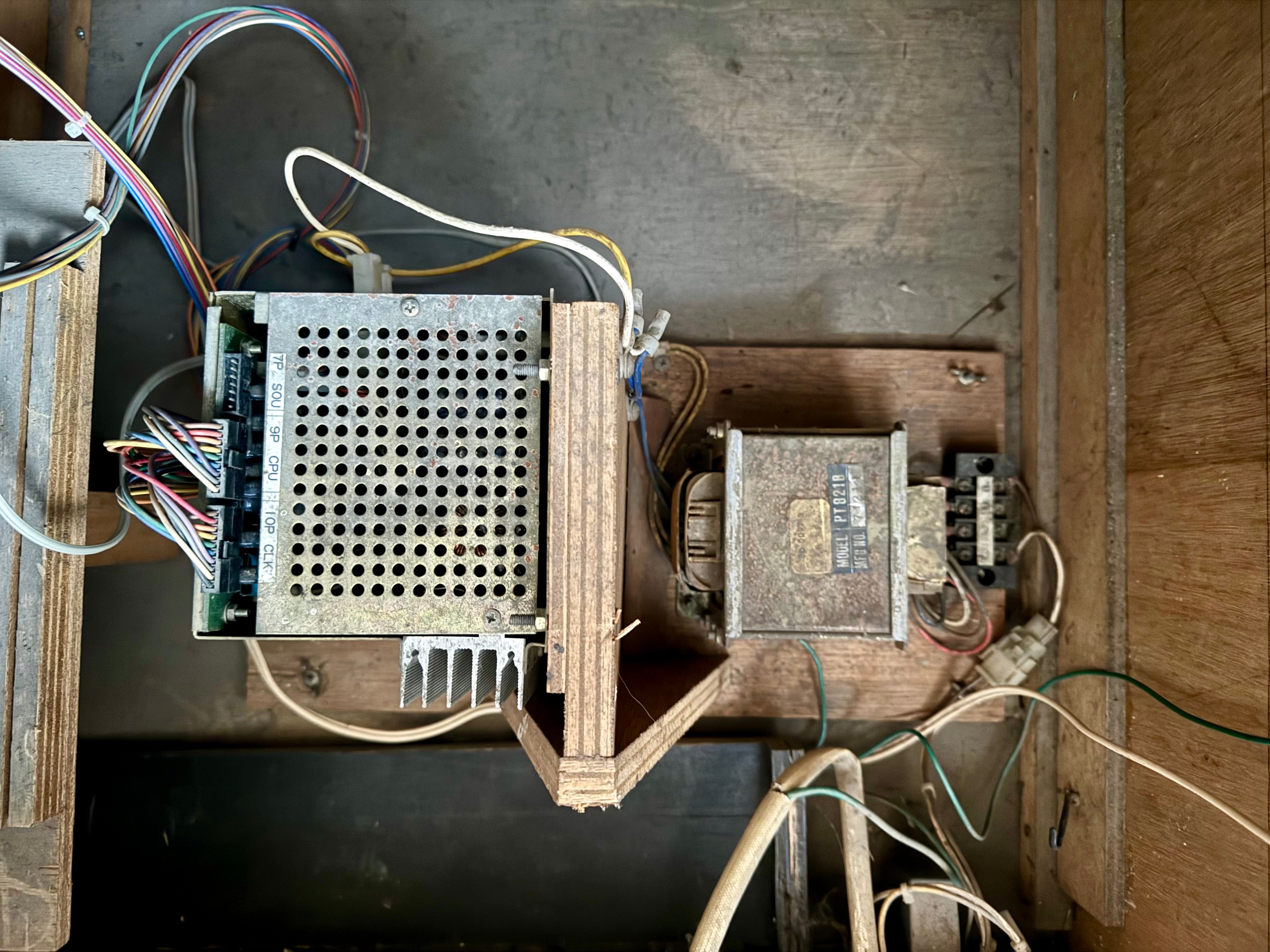
2. Key Components of an Arcade Power Supply
A PSU consists of several essential parts that regulate and distribute power throughout the arcade machine.
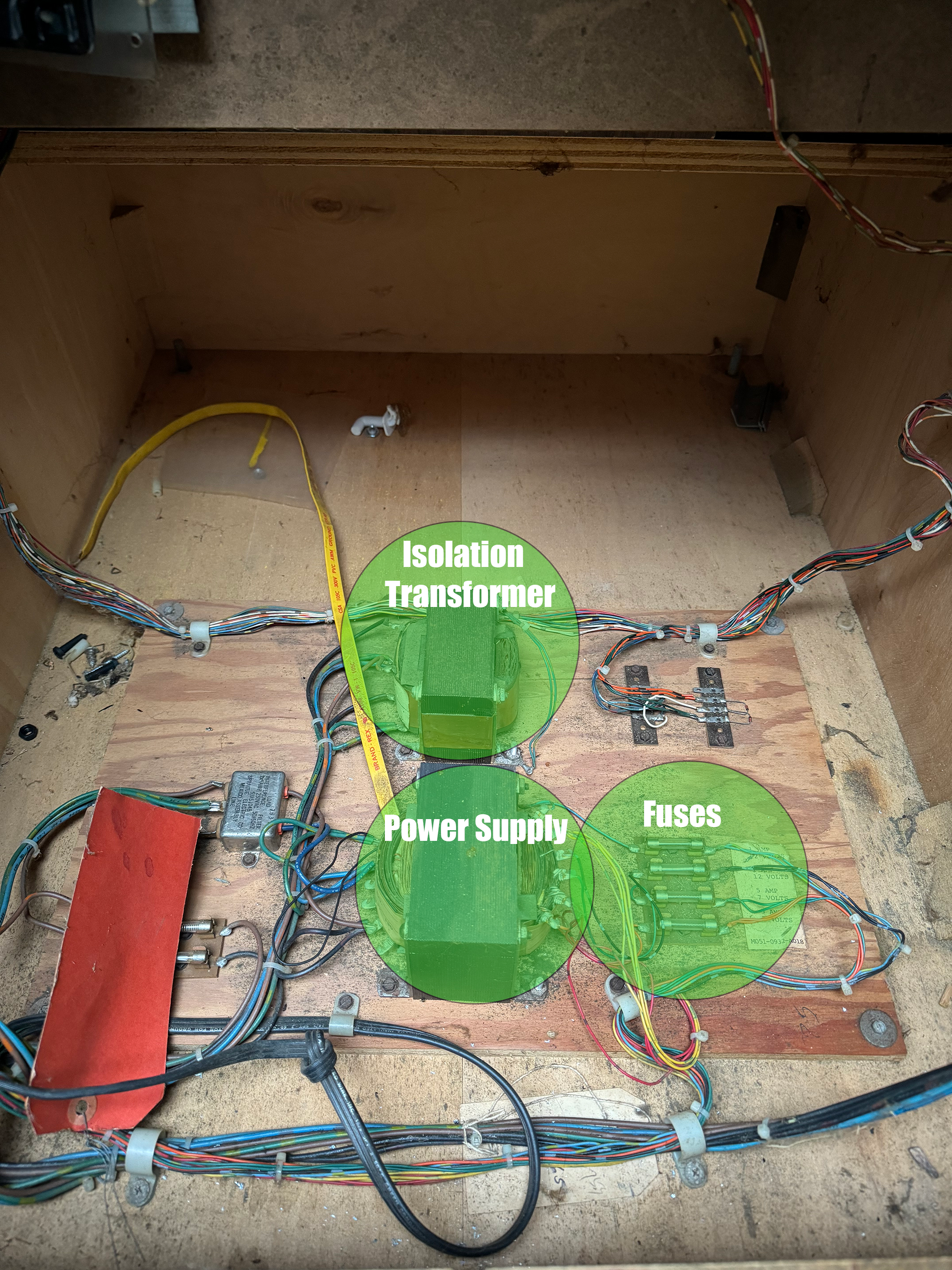
Transformer
- Converts high-voltage AC from the wall into a lower voltage needed by the arcade components.
- In linear PSUs, transformers are large and heavy; switching PSUs use smaller, more efficient transformers.
Rectifier & Voltage Regulators
- Converts AC to DC power.
- Provides stable voltage outputs to prevent damage to arcade boards.
Capacitors
- Store and regulate voltage to smooth out power delivery.
- Aging capacitors can cause voltage drops, instability, or failure to boot.
Fuse & Protection Circuitry
- Prevents overvoltage or short circuits from damaging components.
- A blown fuse often indicates a power surge or internal PSU failure.
Voltage Adjustment Potentiometer
- Allows fine-tuning of +5V, +12V, and -5V outputs to meet PCB requirements.
- Incorrect voltage settings can lead to game crashes or hardware damage.
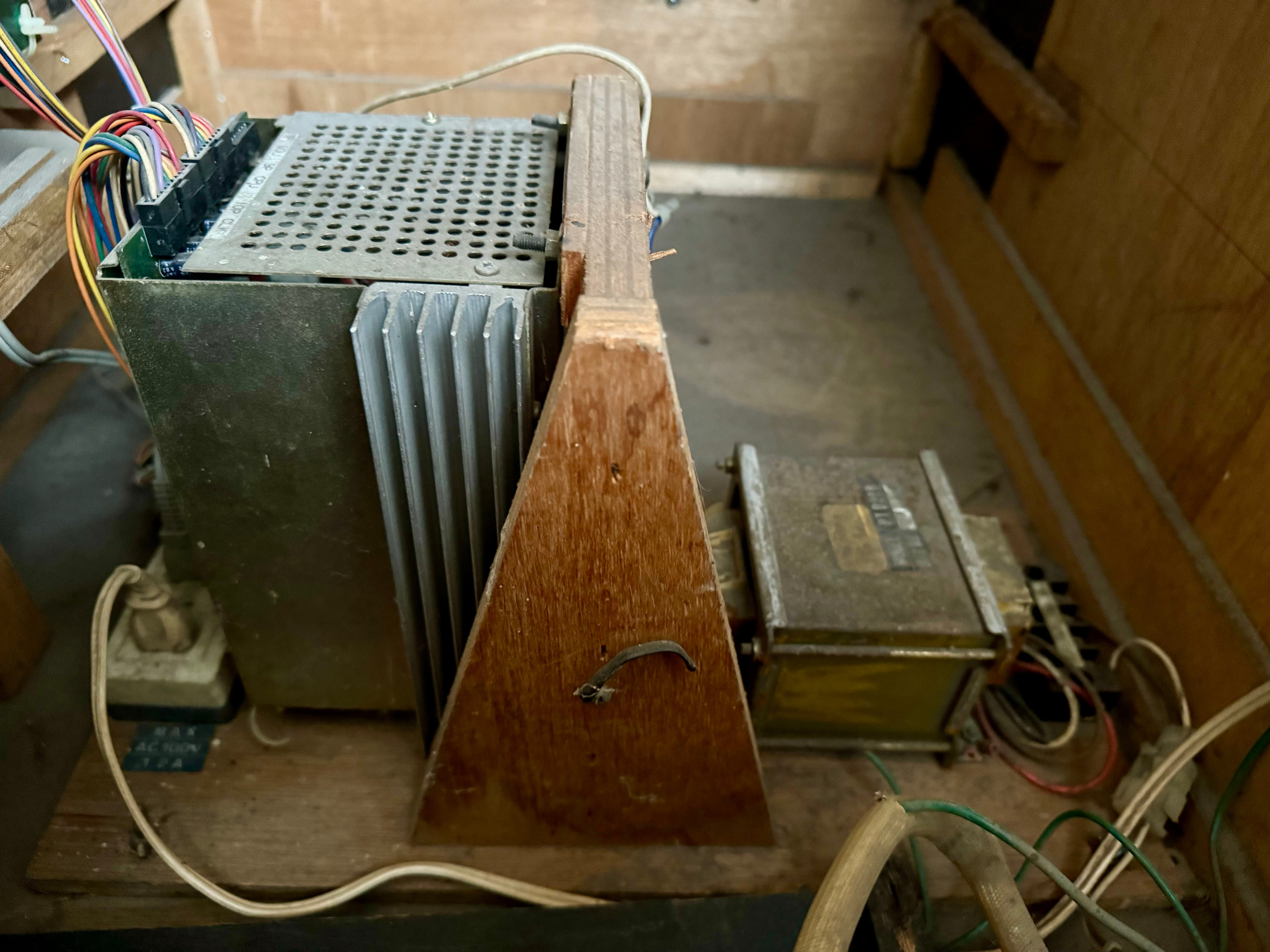

3. How an Arcade PSU Works
- AC power enters the PSU and passes through a fuse.
- The transformer reduces voltage to safer levels.
- The rectifier converts AC to DC for stability.
- Regulators fine-tune voltages to match the arcade PCB requirements.
- The PCB, monitor, and controls receive power, allowing gameplay.
4. Common PSU Issues & Troubleshooting
Symptoms of PSU Failure:
- No Power / No Boot – Could be a blown fuse or failed PSU.
- Graphics Glitches / Freezing – Low or unstable voltage.
- Flickering Monitor / Dim Screen – Insufficient power reaching the CRT.
- No Sound – Issues with the +12V rail for audio.
How to Diagnose PSU Issues:
- Check the fuse – Replace if necessary.
- Measure voltages using a multimeter.
- Inspect for bulging capacitors or a buzzing transformer.
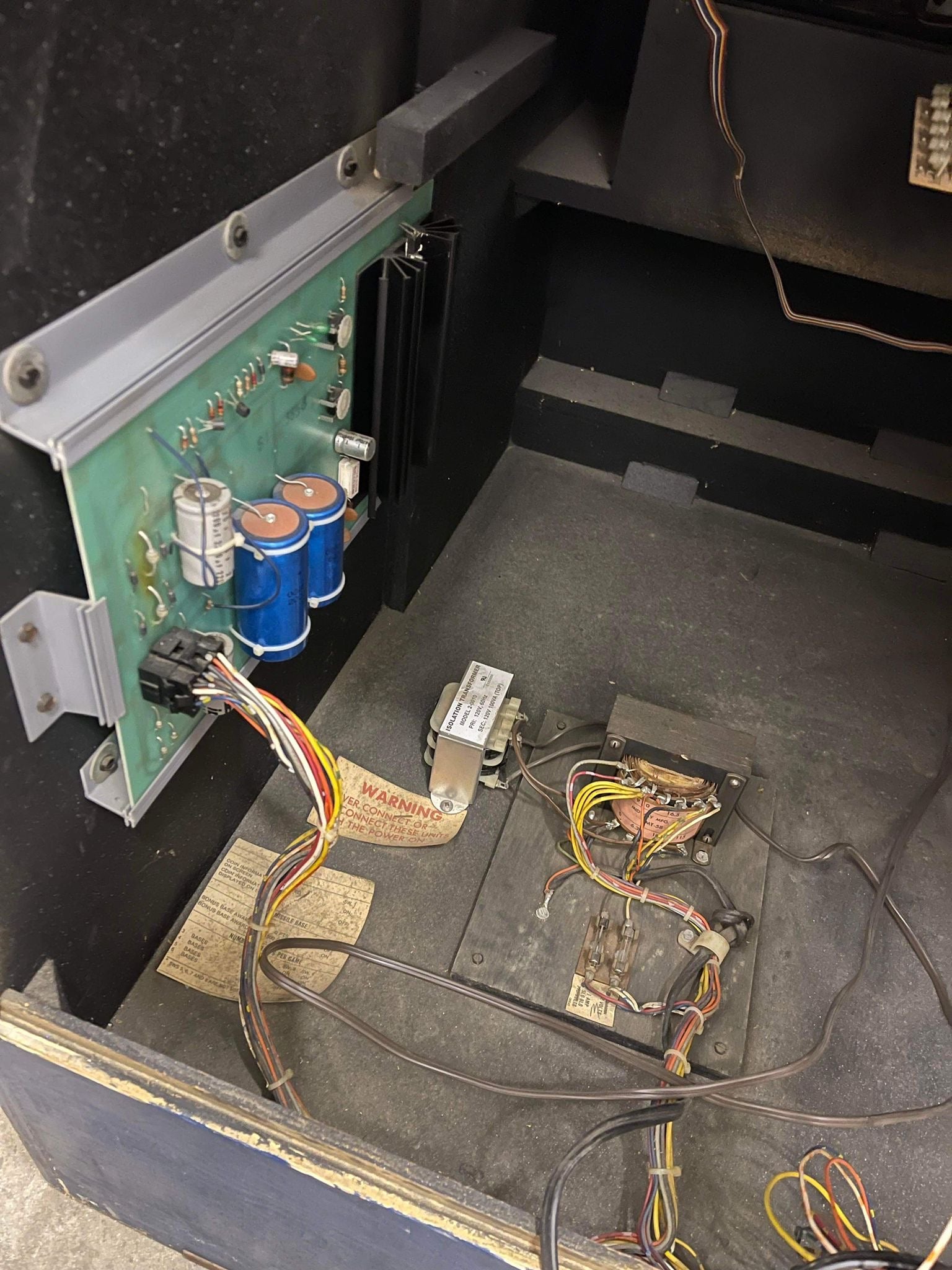
5. Replacing & Maintaining an Arcade PSU
When to Replace a PSU:
- If voltages are unstable or incorrect.
- If capacitors are leaking or bulging.
- If the machine randomly resets or crashes.
Steps to Replace an Arcade PSU:
- Power off and unplug the machine.
- Discharge stored electricity (especially for CRT monitors).
- Disconnect and remove the old PSU.
- Mount and wire the new PSU correctly.
- Adjust the voltage settings using a multimeter.
- Power on and test to ensure stable operation.
6. Linear vs. Switching Power Supplies
Linear PSUs:
- Pros: Simple, long lifespan.
- Cons: Heavy, inefficient, generates heat.
Switching PSUs:
- Pros: Smaller, more efficient, widely available.
- Cons: Can fail suddenly; cheaper models may introduce electrical noise.
For most arcade restorations, switching PSUs are the preferred choice.

7. Conclusion & Next Steps
Arcade power supplies are essential for maintaining stable power across the machine. Proper maintenance and troubleshooting can prevent downtime and extend the lifespan of an arcade cabinet.

